|
When you configure TCP-Com as either a TCP/IP client or a
server, you can control how bi-directional data is handled.
In the TCP/IP settings section of each session window, there
is a button with the caption "I/O Options" that
will open an options dialog box.
Server Options:
When TCP-Com is configured as a TCP/IP Server, clicking the
"I/O Options" button will present the following
dialog box:
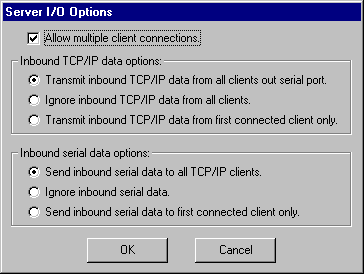
As a server, TCP-Com can accept multiple connections to a
TCP/IP port from any number of clients. You can disable this
functionality and only accept a single client connection by
clearing the check box marked "Allow multiple client
connections". You can also control how bi-directional
data is handled from each connected client using the "Inbound
TCP/IP data options" and the "Inbound serial data
options". The meaning of each option is described below:
Inbound TCP/IP data options:
1. Transmit inbound TCP/IP data from all clients out the
serial port.
This option instructs TCP-Com to accept incoming data from
all connected TCP/IP clients and thus send all data received
out the serial port. Data received from all clients is transmitted
out the serial port as it is received.
2. Ignore inbound TCP/IP data from all clients.
This option instructs TCP-Com to discard all data received
from all connected clients. This effectively turns TCP-Com
into a one-way communications program. This option should
be selected when you want to allow all connected clients to
be able to receive data that is sent by a device into the
serial port however you do not want any of the clients to
be able to send anything out the serial port back to the serial
device.
3. Transmit inbound data from first connected client only.
This option instructs TCP-Com to allow only the first connected
client to have the ability to transmit data out the serial
port. Any clients that establish a connection to TCP-Com after
the first client connects will only be able to see incoming
serial data and will not be able to send any data out the
serial port.
Inbound serial data options:
1. Send inbound serial data to all TCP/IP clients.
This option instructs TCP-Com to send incoming serial data
to all connected TCP/IP clients.
2. Ignore inbound serial data.
This option instructs TCP-Com to discard all data received
through the serial port. This option should be selected only
when you want to allow all connected clients to be able to
transmit data out the serial port to a device however you
do not want any of the clients to be able to receive any data
back from the serial device.
3. Send inbound serial data to first connected client only.
This option instructs TCP-Com to allow only the first connected
client to have the ability to receive data from the serial
port. Any clients that establish a connection to TCP-Com after
the first client connects will only be able to send data out
the serial port.
Client Options:
When TCP-Com is configured as a TCP/IP Client, clicking the
"I/O Options" button will present the following
dialog box:
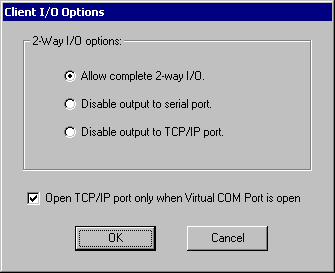
As a client, TCP-Com establishes a connection to a TCP/IP
server. Normally any data received through the TCP/IP port
that it connects to would be transmitted out the serial port
and any data received through the serial port is sent back
to the TCP/IP server. You can choose to enable or disable
full 2-way communications using the following options:
1. Allow complete 2-way I/O.
This option enables fully bi-directional communications.
2. Disable output to serial port.
Selecting this option causes TCP-Com to discard all data received
from the TCP/IP server that it is connected to and thus not
send any data out the serial port.
3. Disable output to TCP/IP port.
Selecting this option causes TCP-Com to discard all data received
through the serial port and therefore not send any serial
data to the TCP/IP server.
Checking the checkbox labeled “Open TCP/IP port only
when Virtual COM port is open” causes TCP-Com to open
the TCP/IP client connection only when a serial communications
program has opened the Virtual COM port. This option only
applies if you have TCP-Com configured to create a Virtual
COM port. If the application that has the Virtual COM port
opened closes the virtual COM port, then TCP-Com will also
close the TCP/IP client connection.
If you disable this option, then TCP-Com will open the TCP/IP
client connection as soon as you activate it however any data
received over the TCP/IP port will be discarded until another
serial communications program opens the Virtual COM port.
See
Also:
Welcome to TCP-Com
Common Applications for TCP-Com
Configuring TCP-Com
TCP/IP Client and Server Options
TCP-Com Advanced Options
Using the Ping Tool
Using the Resolve Host Address
Tool
Saving and Loading TCP-Com configuration
files
Password Protecting TCP-Com
Configuring TCP-Com to run as
a Windows Service
Interfacing RS232 Instruments
to a TCP/IP Network
Using TCP-Com to send/receive
data over the Internet
A Very Basic Overview of
TCP/IP Communications
|
